Introduction
In the landscape of nutritional support, enteral and parenteral nutrition stand as 2 primary methods for delivering essential nutrients to individuals that can not satisfy their dietary needs through requirement oral consumption. This short article explores the distinctions between these two forms of nourishment, clarifying their meanings, applications, benefits, and training viewpoints. With an expanding focus on tailored dietary support, understanding these differences is vital for healthcare specialists, especially those involved in nursing and allied health.
Understanding the Differences Between Enteral and Parenteral Nutrition: A Training Perspective
Enteral nutrition (EN) refers to the distribution of nutrients directly into the intestinal tract, generally with a feeding tube such as a PEG (Percutaneous Endoscopic Gastrostomy) tube. In contrast, parenteral nutrition (PN) includes providing nutrients intravenously, bypassing the digestive system completely. This basic difference influences every little thing from person selection to training demands for healthcare providers.
What is Enteral Nutrition?
Enteral nutrition is made for individuals who have operating digestive system systems but are unable to consume food by mouth as a result of clinical problems such as stroke, neurological conditions, or dysphagia. EN can be provided by means of various techniques:
- Oral Supplements: Nutritional consumes alcohol that supplement meals. Feeding Tubes: Including nasogastric tubes (NG), gastrostomy tubes (PEG), and jejunostomy tubes.
What is Parenteral Nutrition?
Parenteral nutrition accommodates individuals that can not utilize their intestinal systems properly as a result of problems like digestive tract obstruction or serious pancreatitis. PN offers total dietary support with:
- Total Parenteral Nutrition (TPN): An intricate blend of carbohydrates, proteins, fats, vitamins, and minerals supplied directly into the blood stream by means of central venous access.
The Significance of Training in Nutritional Support
As medical care comes to be progressively specialized, training procedures are important in guaranteeing risk-free and reliable management of both enteral and parenteral nutrition. Specialized courses like the NDIS PEG Feeding Training and enteral feeding support programs gear up nurses and assistance employees with necessary skills.
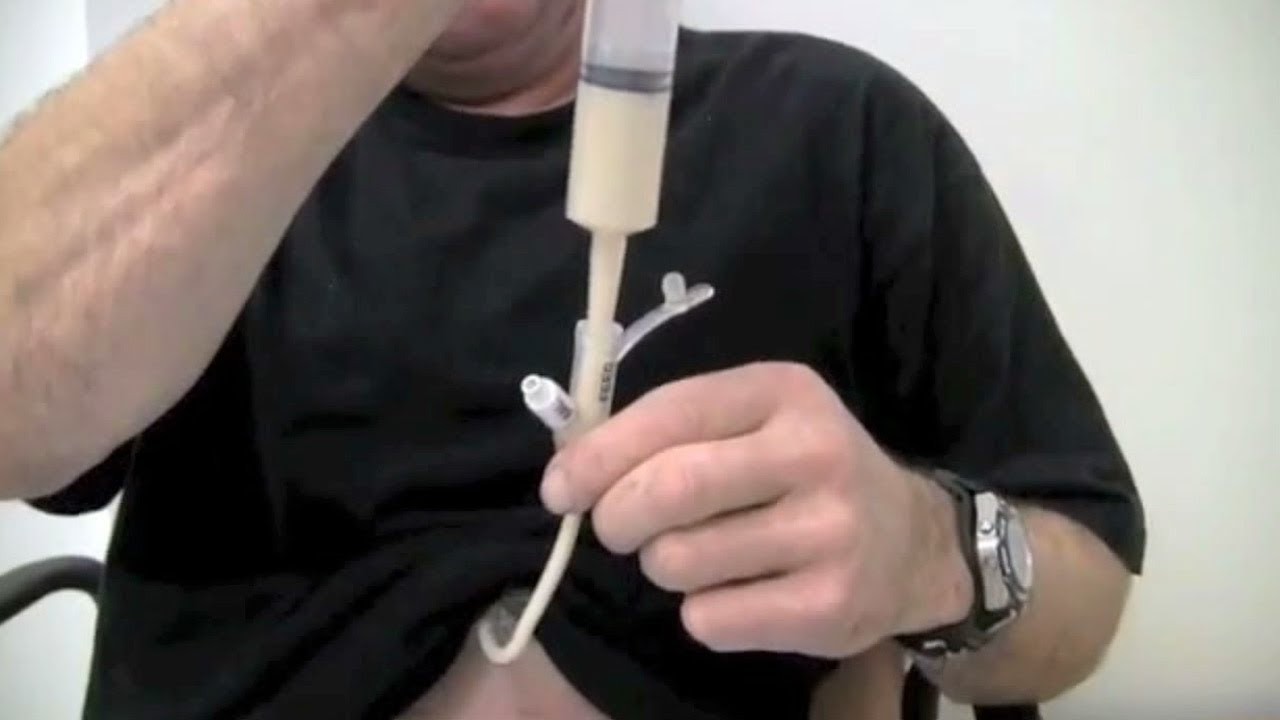
Enteral Feeding Support Program Overview
This training course focuses on:
- Assessing person demands for enteral feeding. Learning about different kinds of enteral formulas. Practical skills for tube insertion and maintenance.
PEG Training for Nurses
Nurses play an important role in handling individuals with PEG tubes. Training consists of:
- Understanding indicators for PEG placement. Techniques for safe tube care. Recognizing complications such as infections or blockages.
Comparative Analysis of Enteral vs. Parenteral Nutrition
|Facet|Enteral Nourishment|Parenteral Nutrition|| -------------------------------|--------------------------------------|---------------------------------------|| Course|Intestinal system|Intravenous|| Indications|Practical GI system|Non-functional GI tract|| Nutrient make-up|Whole foods/formula|Personalized TPN service|| Danger elements|Tube-related complications|Infection danger from IV gain access to|| Expense|Normally reduced|Higher due to complicated solutions|
Benefits of Enteral Feeding over Parenteral Feeding
Preservation of Digestive tract Integrity: EN maintains digestive tract function by promoting mucosal integrity. Lower Infection Risks: Contrasted to PN, EN has actually a minimized threat of infections since it does not entail capillary access. Cost-effectiveness: EN normally costs much less than PN due to less needed resources.When is Parenteral Nourishment Necessary?
While enteric courses are liked when possible, PN ends up being needed in scenarios such as:
- Severe malabsorption syndromes. Inflammatory bowel condition exacerbations. Short bowel syndrome adhering to medical resections.
Key Elements of Effective Enteral Feeding Training Programs
Training programs must integrate detailed curricula covering multiple aspects:
1. Makeup and Physiology Pertaining To Digestive Health
Understanding just how the intestinal system works makes sure experts can make informed decisions relating to feeding methods.
2. Analysis Skills
Healthcare carriers require training in analyzing indicators that determine whether a patient needs enteric or parenteric feeding options.
3. Tube Monitoring Techniques
Learning correct methods for insertion and monitoring minimizes risks View website related to feeding tubes.
4. Keeping Track Of Client Progress
Regular monitoring helps evaluate dietary status while changing plans based upon private responses.
FAQs Concerning Enteral and Parenteral Nutrition
1. What is PEG Feeding?
PEG feeding refers specifically to supplying nutrients through a percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy tube put straight into the stomach.
2. When ought to I take into consideration using an enteral feed?
Consider making use of an enteric feed when an individual has a practical stomach system yet can not take in food by mouth as a result of numerous health issues.

3. What are some typical issues connected with PEG feeds?
Common complications include infection at the insertion site, tube dislodgment or obstruction, and desire pneumonia if feeds are not managed correctly.
4. For how long can a private remain on parenteral nutrition?
Patients can stay on parenteral nourishment forever if very closely kept track of; nevertheless, lasting usage may result in problems like liver damages or nutrient deficiencies.
5. Can enterally fed patients additionally obtain dental intake?
Yes! Numerous individuals may still consume percentages by mouth if they have some swallowing capability; this need to always be assessed individually.
6. What certifications are readily available for experts handling PEG feeds?
Various programs use qualification in PEG feeding techniques consisting of peg feeding training courses details to Australia that provide necessary understanding and skills.
Conclusion
Understanding the differences between enteral and parenteral nourishment from a training viewpoint is essential for medical care specialists who aim to offer optimum look after their patients calling for nutritional support. Both methods have distinct applications which highlight their unique roles within professional setups-- making sure that despite the approach used, individuals obtain safe and reliable nutritional therapy tailored to their individual needs.
